Hosting Maps Assets in Azure Blob Storage with CORS enabled
You'll see references in the Icon Map Pro and Icon Map Slicer documentation about one of the hosting requirements for images etc to have CORS configured. This blog post goes through the process of setting up Azure Blob Storage and configuring CORS as a cost effective way of hosting these items.
What is CORS and Why It Matters
When you build web applications that fetch data or images from a server, your browser enforces something called the Same-Origin Policy. This is a security rule that stops your website from directly requesting resources from a different domain unless that other domain explicitly says it’s okay.
CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) is the system that makes those exceptions possible. It’s like the “guest list” at a party—if your domain is on the list, the server will allow your browser to load the file.
Without CORS configured, your map visuals in Power BI—whether they’re loading GeoJSON files for boundaries or images for custom markers—will fail with errors like “No ‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’ header”. This is because the browser blocks the request before the data even reaches your code.
By enabling CORS in Azure Blob Storage, you’re telling Azure:
“It’s fine for browsers running my Power BI reports to fetch these resources.”
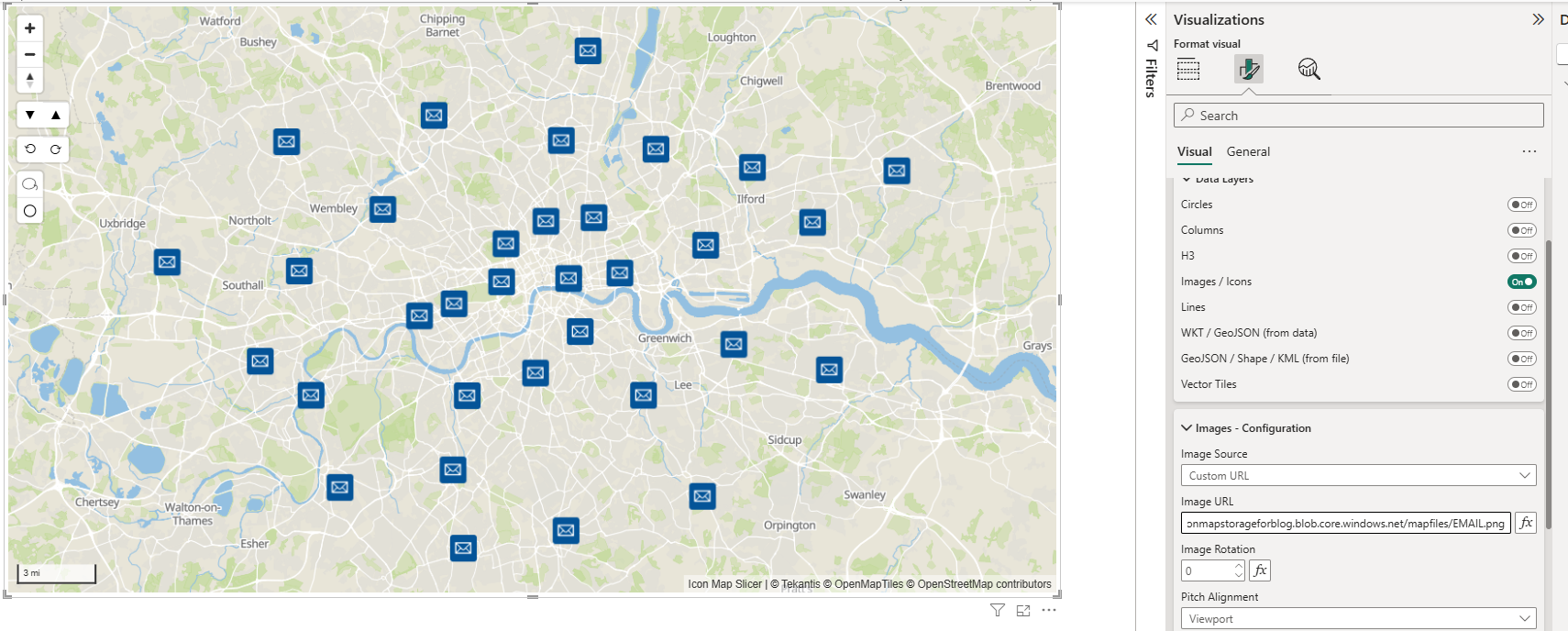
That way, the Icon Map Pro and Icon Map Slicer visuals (built on MapLibre) can load the hosted assets without a hitch, even though they’re coming from a different domain than the Power BI service.
Sandboxing in Power BI and Why the Origin Must Be * or null
When a custom visual runs in Power BI, it doesn’t have full access to the page or browser environment. Instead, it’s sandboxed—meaning it runs inside an isolated <iframe> with tight security restrictions. This prevents malicious visuals from accessing sensitive data or interfering with other parts of the report.
One side effect of sandboxing is that the visual’s requests often come from a special, isolated origin that isn’t the same as the domain hosting your Power BI report. In many cases, this origin is treated as null by the browser. That means if your Azure Blob Storage CORS settings are locked to a specific domain, the request will be blocked.
To ensure your Power BI visuals can load external resources like images or GeoJSON files, you need to allow requests from either:
*— which means “allow any origin”null— which specifically allows sandboxed or local file requests
In practice, setting the CORS origin to * is the most common choice for public, non-sensitive assets, as it ensures compatibility with the Power BI sandbox environment and avoids mysterious CORS errors when loading resources.
Setup Azure Blob Storage
Why use Azure Blob Storage for hosting map assets
Azure Blob Storage is a fast, reliable, and cost-effective way to host the static files your map visuals need, such as images, GeoJSON files, or PMTiles. It gives you secure HTTPS URLs, global availability, and straightforward CORS configuration so your Power BI visuals can access the files without issues. You can make assets public for easy sharing or use access controls for private content.
Create a Storage Account
From within the Azure Portal click the "Create a resource" button:

and then choose to create a Storage Account
Choose your Azure Subscription, create a Resource Group (or select an existing one). Give your storage account a name, and choose a region - I'd suggest the same one as your Power BI tenant. Select Azure Blob Storage as your primary service:
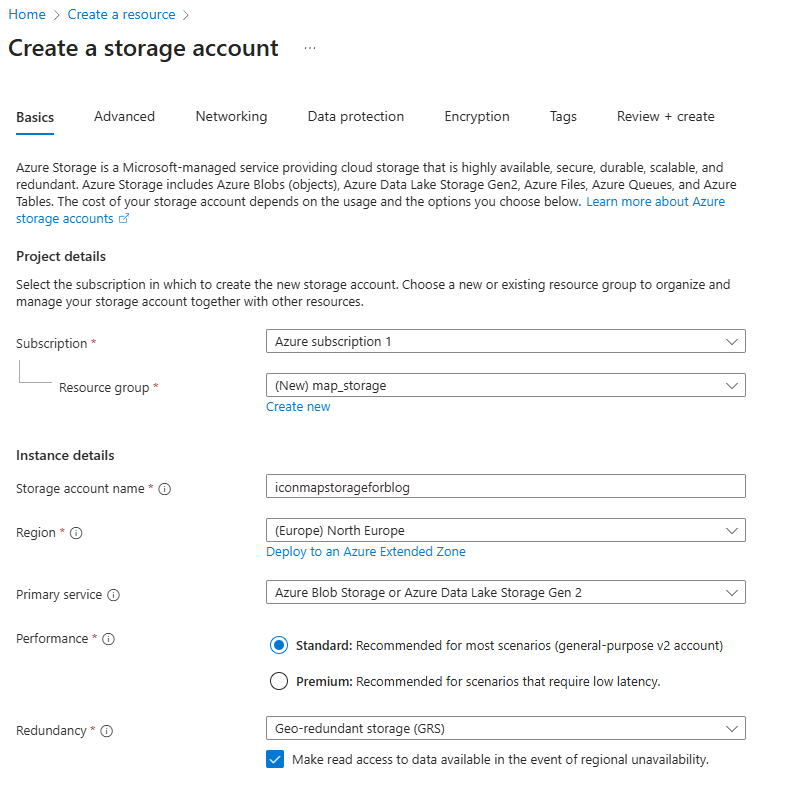
Then click Review + Create. And once validated, hit the "Create" button.
Now Azure will create and deploy your storage account. This will likely take a couple of minutes.
Once it's completed you can click the "Go to resource" button.
Configure Anonymous Access
On the left hand menu, you'll find "Configuration" in the Settings menu.
Enable "Allow Blob anonymous access".
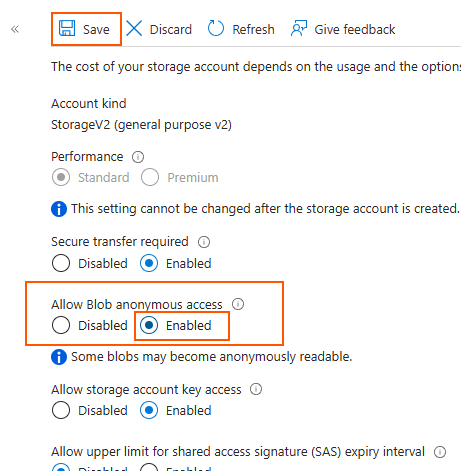
This allows public access to the files in your storage account. This isn't necessary if you use SAS tokens, but this isn't covered in this blog post.
Configure CORS
Before we worry about uploading our files, let's get the CORS configuration out of the way.
On the left hand menu, you'll find Resource sharing (CORS) in the Setting menu:
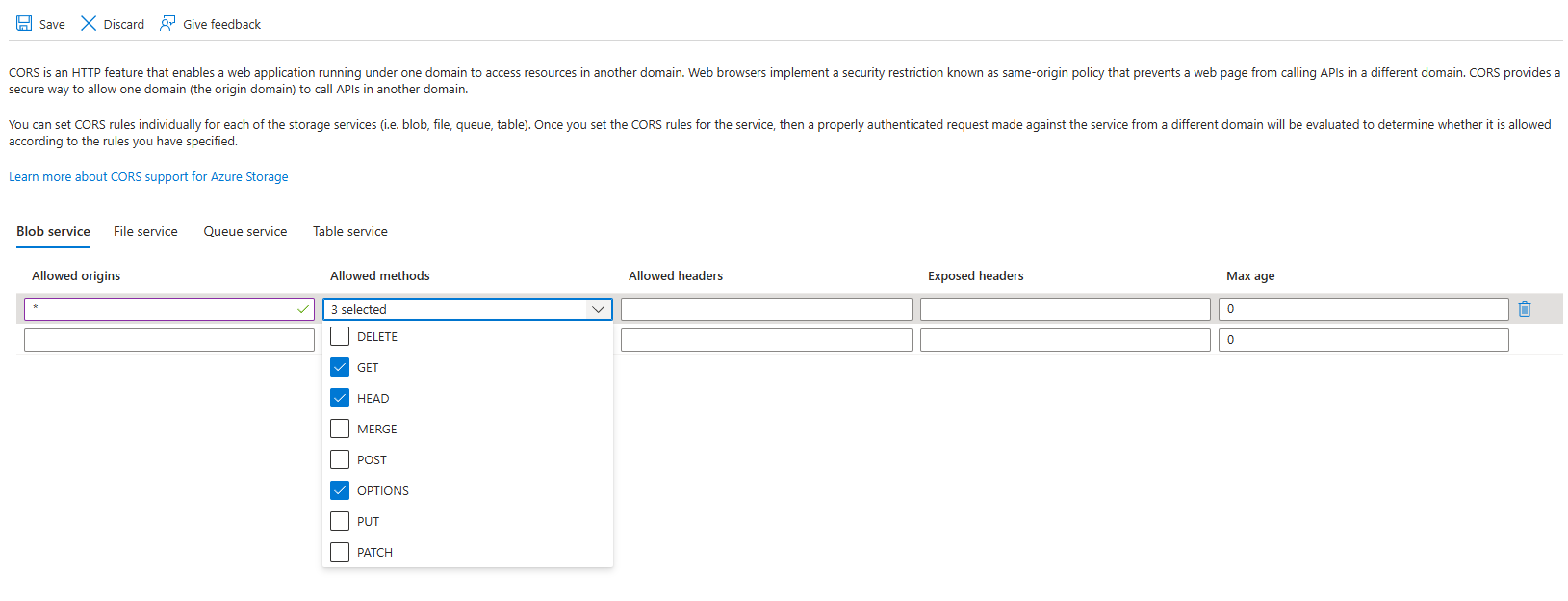
Then configure the Blob service as follows. Enter null or * for allowed origins; GET, HEAD and OPTIONS for Allowed methods, then hit the Save button.
Setup the container
Now we're ready to set up our storage container to host our assets. Navigate to Data Storage -> Containers in the menu:
Hit the Add Container button
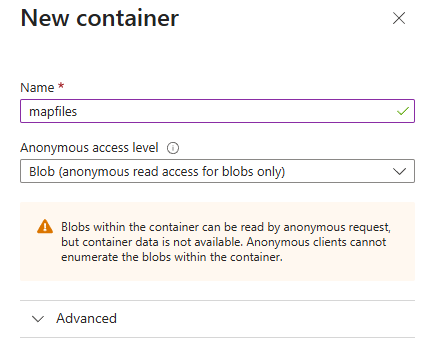
Give your container a name and select "Blob (anonymous read access for blobs only)" from the Anonymous access level dropdown.
Upload your files
Now click on the newly created container to enter it.
Use the "upload" button to add your resource.
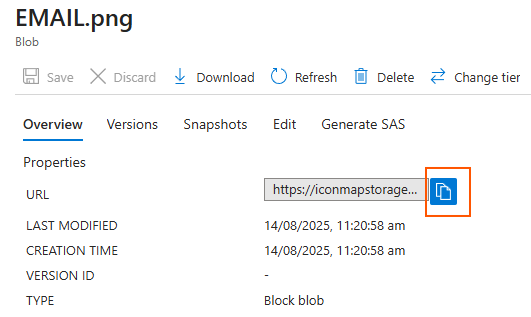
Once uploaded, you can click on your file to see the details. You can then click the URL icon to copy the URL to paste into Icon Map Pro or Icon Map Slicer: